Let Us YOU Solve Physics JEE (MAIN) 2018 Physics Paper
We are into a new blog, and as a continuation from the previous blog, we guide you to solve more Physics questions from JEE (Main) 2018, Paper-1. These are all MCQs with a single correct option, and you crack them based on the theories learnt fresh from the oven – oops! From the video lectures @ www.PhysicsAcademyOnline.com.
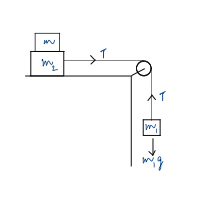
Question 3: Two masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 10 kg, connected by an inextensible string over a frictionless pulley, are moving as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction of horizontal surface is 0.15. The minimum mass m that should be put on top of m2 to stop the motion is:
(1) 18.3 kg (2) 27.3 kg (3) 43.3 kg (4) 10.3 kg
Initially, when (m1 + m2) system moves, what are the forces causing and resisting its motion? Subscribe to www.PhysicsAcademyOnline.com, and watch the lecture: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Newton’s Laws of Motion; Video Name – Free Body Diagram.
Draw the free body diagrams of m1 and m2 . Write their respective equations of motion, and hence the equation of motion for the system. When mass m is placed on m2 , which force changes and to what value? Open the lecture: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Friction; Video Name – Static and Kinetic Friction.
What condition must be fulfilled if the motion has to stop eventually?
Question 5: In a collinear collision, a particle with an initial speed v0 strikes a stationary particle of the same mass. If the final total kinetic energy is 50% greater than the original kinetic energy, the magnitude of the relative velocity between the two particles, after the collision, is:
(1) v0/4 (2) √2. v0 (3) v0/2 (4) v0/√2
This is an uncommon “superelastic” collision, in which the final kinetic energy of the particles exceeds the initial kinetic energy. But energy remains conserved or not, which quantity will remain conserved during the collision? Study the lecture: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Impulse, Collision, and Centre of Mass; Video Name – Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum, and Some Applications.
Apply the conservation principle to get an equation involving initial speed v0 and final speeds v1 and v2 . What is the formula for kinetic energy of a particle? It’s here: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Work and Energy; Video Name – Concept of Energy, and Derivation of Work-Energy Theorem.
Use the condition given in the question to obtain one more equation involving v0 , v1 and v2 . Manipulate the two equations to find relative velocity, (v2 – v1). The video solution below shows a little algebraic jugglery!
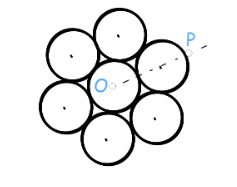
Question 6: Seven identical discs, each of mass M and radius R, are welded symmetrically, as shown in figure. The moment of inertia of the arrangement about the axis normal to the plane of the discs and passing through the point P is:
(1) 19 MR2/2 (2) 55 MR2/2 (3) 73 MR2/2 (4) 181 MR2/2
What is the formula for moment of inertia of a uniform disc about a normal through its centre? Find from the lecture: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Rotational Mechanics; Video Name – Moment of Inertia, and Its Calculation for Various Bodies.
Now, what is the moment of inertia of the central disc about O? What is the moment of inertia of each of the six surrounding discs about O? You will require to watch: Chapter Name – Mechanics; Category – Basic; Topic Name – Rotational Mechanics; Video Name – Two Important Theorems on Moment of Inertia.
What is the total moment of inertia of the seven-disc system about O? Hence, what is the total M.I. about P? Confirm your answer from the video solution.